Using dietary changes and nursing interventions, this hypokalemia NCP treats symptoms. Low potassium levels, or hypokalemia, compromise muscular performance, neuron activity, and heart rhythm. Untreated, it can cause arrhythmias, extreme weakness, or respiratory failure. Diuretics raise the danger of potassium loss, hence monitoring and education are rather important. Patients’ quality of life is enhanced and potassium levels are maintained with a well-organized hypokalemia nursing care plan.
Table of Content:
- Hypokalemia NCP: Patient Scenario and Its Impact
- Patient Education on Hypokalemia NCP
- Comprehensive Assessment for Hypokalemia NCP: Nursing Care Plan
- NANDA Nursing Diagnosis for Hypokalemia NCP
- Care Plan Goals for Hypokalemia NCP: Nursing Diagnosis and Management
- Nursing Interventions for Hypokalemia NCP: Managing Low Potassium Levels
- Evaluation of Nursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia NCP: Assessing Patient Progress
- References of Nursing Care Plan Hypokalemia
Download the Hypokalemia NCP in PDF
You can download the hypokalemia NCP in PDF format by clicking on the Download button at the end of this post.
Hypokalemia Ncp in picture form is given below to help students:
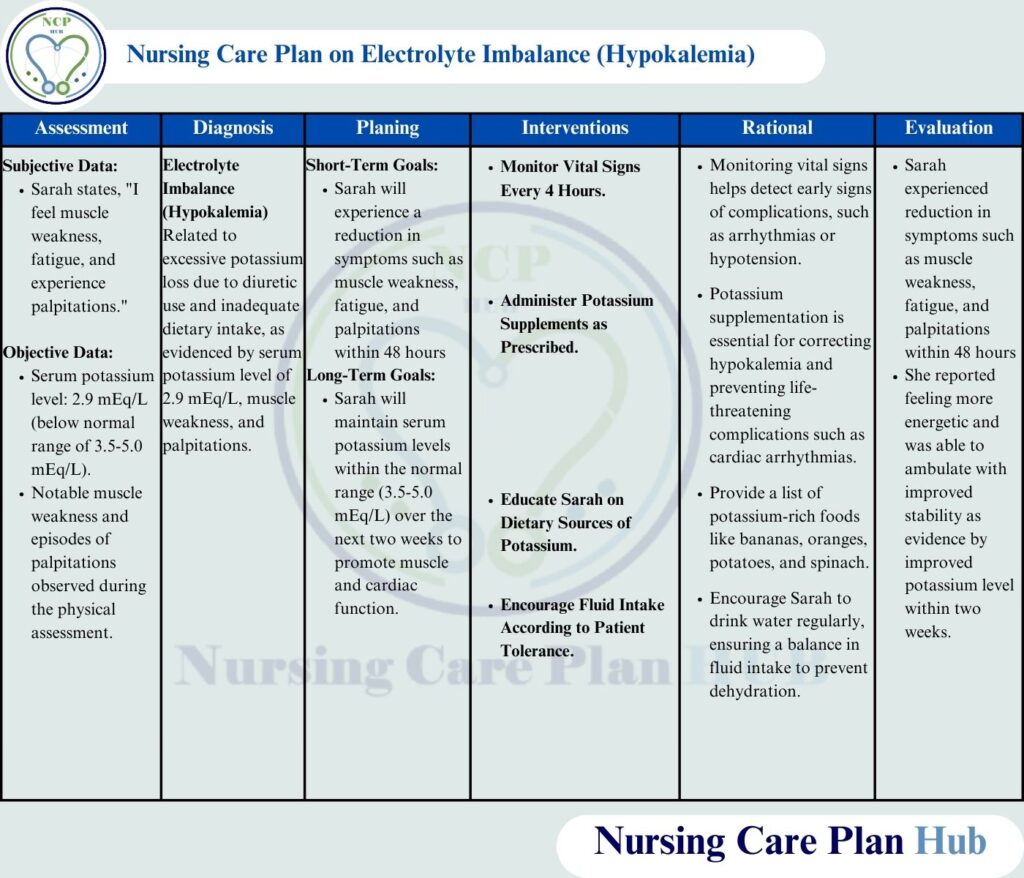
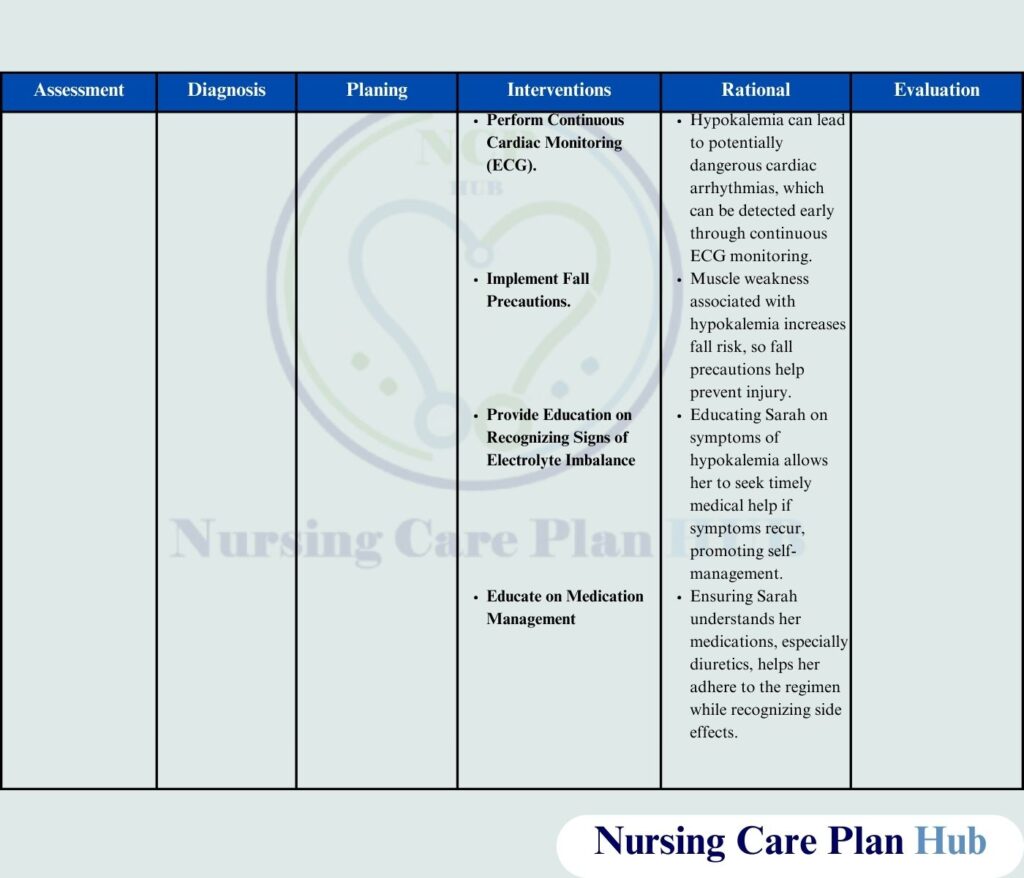
Hypokalemia NCP: Patient Scenario and Its Impact
Sarah, a 50-year-old female, was admitted to the hospital with complaints of fatigue, muscle weakness, and occasional palpitations. She has been prescribed a thiazide diuretic, which is known to cause potassium loss; she also has a history of hypertension. Lab studies verified hypokalemia with a 2.9 mEq/L potassium level. In her diet, Sarah generally eats processed foods, she consumes few fruits and vegetables naturally high in potassium. Her doctor has prescribed changes in diet and potassium drugs to help restore balance and prevent any further issues.
Sarah’s hypokalemia NCP calls for everyday life’s impacts, like weariness and physical cramps, to be taken under consideration. Unchecked, hypokalemia can cause cardiac issues. Correct therapy needs for dietary adjustments, awareness of foods heavy in potassium, prescription changes, and frequent monitoring. A good hypokalemia nursing care plan helps restore strength and maintains potassium balance.
Patient Education on Hypokalemia NCP
What is Hypokalemia?
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines hypokalemia as a disorder whereby the potassium content in the blood is below normal, therefore influencing cellular activities, especially in muscles and the heart (World Health Organization, 2023). Preventing problems depends on keeping enough potassium levels. A well-organized hypokalemia nursing care plan guarantees patients get appropriate monitoring and treatment to avoid major consequences.
Pathophysiology of Hypokalemia NCP
When potassium levels fall below 3.5 mEq/L, hypokalemia results. Maintaining cellular activity, neuron function, and muscular contraction depend on potassium. Diuretics such as thiazides, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), raise urine potassium excretion, which causes potassium shortage and symptoms include cardiac abnormalities and weakness. Appropriate nursing interventions for hypokalemia can assist to restore potassium balance and avoid consequences.
Causes of Hypokalemia
Common causes include chronic renal disease (American Society of Nephrology, 2022), gastrointestinal losses (e.g., vomiting, diarrhea), inadequate dietary intake of potassium, and too strong diuretic usage. Long-term diuretic patients should monitor potassium levels and minimize deficits by following a hypokalemia nursing care plan.
Risk Factors of Hypokalemia NCP
A number of elements raise a person’s risk of hypokalemia. These include low dietary potassium, high salt consumption, certain drugs (e.g., diuretics), too much sweating, and underlying diseases (World Health Organisation, 2023). Effective nursing interventions for hypokalemia help to lower the possibility of problems by teaching patients about these risk factors. Nurses are thus very important in this regard.
Symptoms of Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
Early management depends on an awareness of the hypokalemia symptoms. Typical symptoms are: muscular weakness; fatigue
In extreme cases, paralysis (National Institutes of Health, 2023); in mild ones, constipation; irregular pulse; cramps
By use of an organized hypokalemia nursing care plan, timely identification and management can assist to prevent major problems and guarantee patient safety.
Complications of Hypokalemia NCP
Severe hypokalemia can cause life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory muscle weakness, and higher risk of consequences from various medical conditions like hypertension (American Society of Nephrology, 2022). Appropriate nursing interventions for hypokalemia center on tracking potassium levels, guaranteeing sufficient food intake, and stopping further loss by means of drug management. Following a hypokalemia nursing care plan would enable doctors to assist patients keep ideal health and avoid major issues.
In summary, early identification, prevention, and efficient therapy of potassium imbalances depend on patient education on hypokalemia NCP. To reduce the dangers related with hypokalemia, healthcare professionals should stress the need of dietary potassium intake, medication adherence, and frequent monitoring. Appropriate nursing interventions for hypokalemia help patients to keep stable potassium levels and enhance their general health results.
Comprehensive Assessment for Hypokalemia NCP: Nursing Care Plan
Monitor Serum Potassium Levels in Hypokalemia NCP
- Rationale: Understanding the degree and course of hypokalemia requires regular monitoring (National Institutes of Health, 2023). Any hypokalemia nursing care plan must include careful maintenance of potassium levels within the normal range.
- How to Perform: Ask for a blood sample and routinely check lab findings to see whether nursing interventions for hypokalemia have any effect. Treatment should be altered depending on trends in potassium.
Assess Dietary Intake for Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Rationale: Evaluating food intake promotes appropriate hypokalemia nursing interventions and helps to identify potassium deficits (American Dietetic Association, 2021). Management of hypokalemia NCP depends much on dietary changes.
- How to Perform: Track daily consumption in a food diary, especially noting the frequency and amount of foods high in potassium—such as bananas, oranges, spinach, and potatoes. As part of her hypokalemia nursing care plan, teach Sarah to add more foods high in potassium to her diet.
Check for Symptoms of Hypokalemia NCP
- Rationale: First, Sarah’s physical status must be known before deciding on the suitable nursing care for her hypokalemia (National Institutes of Health, 2023).
- How to perform? Inquire of Sarah about constipation, heart palpitations, weariness, or muscular weakness. Look physically, evaluating muscular strength and listening for cardiac rhythm irregularities. Early detection of these symptoms facilitates the development of a suitable hypokalemia nursing care plan.
Cardiac Monitoring (ECG) in Hypokalemia NCP
- Rationale: Early diagnosis of arrhythmias is crucial to avoid significant repercussions from hypokalemia significantly influencing the cardiac electrical activity (American Heart Association, 2022). Usually depending on continuous monitoring, a hypokalemia nursing care plan
- How to Perform: To regularly evaluate Sarah’s heart rhythm, it is recommended that she undergo electrocardiogram monitoring, particularly if her potassium level stays low. Quick nursing interventions for hypokalemia are necessary to stabilize heart function in the event that anomalies occur.
Monitor Urine Output and Renal Function in Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Rationale:Hypokalemia can damage renal function; thus, it is essential to maintain urine output and fluid balance to avert further potassium loss (National Kidney Foundation, 2024). Good monitoring is very important in hypokalemia NCP.
- How to Perform: Track Sarah’s daily intake and output, particularly noting any variances suggesting renal failure. Too much urinary potassium loss might worsen hypokalemia and demand adjustments to her hypokalemia nursing care plan.
Evaluate Neurological Status in Hypokalemia NCP
- Rationale: Potassium is very important for nerve function; hypokalemia can lead to numbness, tingling, and confusion (National Institutes of Health, 2024). Effective hypokalemia nursing interventions depend on ongoing neurological symptom evaluation.
- How to Perform: Check Sarah’s orientation, cognitive skills, and any complaints of tingling or numbness. Note any neurological anomalies that might indicate rising hypokalemia and demand rapid nursing interventions for hypokalemia to rectify it.
By effectively monitoring, controlling, and treating hypokalemia, a comprehensive hypokalemia nursing care plan can assist medical practitioners prevent significant outcomes. Nursing interventions for hypokalemia must be timely if they are to guarantee better patient outcomes and long-term potassium balance.
NANDA Nursing Diagnosis for Hypokalemia NCP
A proper hypokalemia nursing care plan begins with an accurate nursing diagnosis. Identifying key patient concerns allows healthcare providers to implement targeted nursing interventions for hypokalemia and prevent complications. Below are essential NANDA nursing diagnoses for hypokalemia NCP:
Imbalanced Nutrition in Hypokalemia NCP
- Diagnosis: Less than Body Requirements Related to Inadequate Potassium Intake Secondary to Hypokalemia, As Indicated by Muscle Weakness and Fatigue (NANDA International, 2023).
- Rationale: Muscle action and energy generation depend on potassium. Low food intake might aggravate hypokalemia, which causes muscles weakness and tiredness. Any hypokalemia nursing care plan depends critically on addressing nutritional deficits.
- Nursing Interventions: Review eating patterns, advise foods high in potassium, and teach patients on preserving appropriate electrolyte balance. These nursing interventions for hypokalemia help to raise nutritional condition and stop further problems.
Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output in Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Diagnosis: Palpitations and abnormalities in the electrocardiogram (ECG) might point to low potassium levels, which would lower cardiac output and hence affect heart function (NANDA International, 2023).
- Rationale: By disturbing regular heart rhythms, hypokalemia can lead to potentially fatal arrhythmias. Correct monitoring and management driven by a structured hypokalemia nursing care plan is absolutely essential.
- Nursing Interventions: Check for palpitations, keep an eye on ECGs, and ensure quick potassium replacement therapy. These nursing interventions for hypokalemia help to maintain cardiac stability and prevent disastrous effects.
Including these NANDA nursing diagnosis for hypokalemia NCP will help nurses to provide effective, patient-centered therapy addressing both nutritional and cardiovascular issues connected with hypokalemia.
Care Plan Goals for Hypokalemia NCP: Nursing Diagnosis and Management
A well-organized hypokalemia nursing care plan depends critically on the clear, realistic goals of the treatment. These objectives ensure that patients acquire appropriate potassium levels and assist direct nursing interventions for hypokalemia, hence preventing problems. Effective treatment of hypokalemia depends on both short-term and long-term targets both here.
Short-Term Goal in Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Goal: Within 48 hours, Sarah will have a decrease in palpitations, muscular weakness, and tiredness (American Society of Nephrology, 2022).
- Rationale: Early management can assist to restore potassium balance, therefore reducing symptoms and avoiding more issues. Any hypokalemia nursing care plan should first address acute hypokalemia symptoms.
- Nursing Interventions: Monitor potassium levels regularly; promote a diet high in potassium; and, when necessary, give potassium pills. These nursing interventions for hypokalemia help to hasten recovery.
Also Read: Nursing Care Plan for Gastroenteritis
Long-Term Goal in Hypokalemia NCP
- Goal: Over the following two weeks, Sarah will keep blood potassium levels within the usual range (3.5–5.0 mEq/L) to support muscular and cardiac activity (American Dietetic Association, 2021).
- Rationale: Preventing hypokalemia from recurrence and guaranteeing best muscle and heart function depend on long-term stability in potassium levels. A organized hypokalemia nursing care plan helps to maintain ongoing health gains.
- Nursing Interventions: Teach Sarah about foods high in potassium; track her adherence to recommended supplements; and run frequent labs to guarantee potassium stability. Long-term treatment depends much on these nursing actions for hypokalemia.
Healthcare professionals may assist patients like Sarah get both immediate symptom alleviation and maintained potassium balance by including these care plan goals for hypokalemia NCP, thereby enhancing the general health outcomes.
Also Read: Nursing Care Plan on Hypertension or High BP
Nursing Interventions for Hypokalemia NCP: Managing Low Potassium Levels
Restoring potassium levels and minimizing consequences depend on using efficient nursing interventions for hypokalemia NCP. A well-organized hypokalemia nursing care plan guarantees patients get suitable treatment to solve potassium deficits and preserve general health. These are basic nursing interventions for hypokalemia NCP that help patients recover.
Administer Potassium Supplements as Prescribed in Hypokalemia NCP
- Rationale: Oral or IV potassium supplements immediately treat low potassium levels, therefore reducing problems such heart arrhythmias (American Heart Association, 2022).
- How to Perform: Use food-based potassium supplements to avoid stomach upset. Use a modest infusion rate if IV administration is needed as fast infusion might be harmful. In the hypokalemia nursing care plan, routinely check blood potassium levels to assess therapy efficacy.
Educate on Potassium-Rich Foods in Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Rationale: Natural sources of potassium are foods such bananas, oranges, spinach, and potatoes; these provide a sustainable approach to keep potassium levels (American Dietetic Association, 2021).
- How to Perform: Talk to Sarah about dinner plans and provide her a list of foods high in potassium. Urge her to include these meals into every meal and provide easy dishes to help adherence. Any hypokalemia nursing care plan depends critically on nutrition.
Monitor Intake and Output (I&O) for Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Rationale: Particularly because diuretics raise urinary potassium excretion, monitoring fluid balance and potassium losses is vital (National Institutes of Health, 2023).
- How to Perform: Daily record all of Sarah’s intake and output; note any notable variations in urine output that would point to too high potassium loss. In the hypokalemia nursing care plan, evaluate for dehydration and modify fluid intake as necessary to maintain electrolyte balance.
Educate on Hypokalemia NCP and Medication Management
- Rationale: Knowing hypokalemia NCP helps people to identify early on hypokalemia symptoms and get quick medical attention. Medication knowledge helps stop more potassium loss (American Society of Nephrology, 2022).
- How to Perform: Share with Sarah typical hypokalemia symptoms include palpitations, muscular weakness, and tiredness. Talk about her present meds and work with her doctor on potassium-sparing substitutes to lower her chance of recurring hypokalemia NCP.
Set Up Continuous ECG Monitoring in Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Rationale: Hypokalemia NCP may lead to serious cardiac dysrhythmias; thus, early identification and management need on constant monitoring (American Heart Association, 2022).
- How to Perform: Set Sarah on ECG monitoring, particularly in light of her still rather low potassium levels. Review ECG values often and quickly let the doctor know if any of the hypokalemia nursing care plan confirms abnormalities.
Also Read: Nursing Care Plan on Insomnia
Encourage Fluid Intake to Support Potassium Balance in Hypokalemia NCP
- Rationale: Particularly for those on diuretics, sufficient fluid intake is crucial for preserving electrolyte balance and balancing potassium levels (National Kidney Foundation, 2023).
- How to Perform: Urge Sarah to avoid too much coffee and sugary drinks and to drink enough liquids every day. In the hypokalemia nursing care plan, appropriate hydration improves kidney function and potassium control.
Administer Potassium-Sparing Diuretics in Hypokalemia Nursing Care Plan
- Rationale: By helping patients using diuretics retain potassium, potassium-sparing diuretics assist reduce potassium loss in them (National Institutes of Health, 2023).
- How to Perform: Make sure Sarah follows recommended potassium-sparing diuretics and routinely checks her potassium levels to keep hyperkalemia free.
With a well-organized hypokalemia nursing care plan, healthcare professionals may assist patients efficiently restore and maintain optimal potassium levels by applying these nursing interventions for hypokalemia NCP, thus lowering the risk of problems and so boosting general well-being.
Evaluation of Nursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia NCP: Assessing Patient Progress
Making sure the patient reaches the intended results depends on assessing the efficiency of the hypokalemia nursing care plan. Constant evaluation enables medical professionals to modify nursing interventions for hypokalemia as necessary. Here is Sarah’s progress assessment after her hypokalemia NCP was started.
- Reduction in Symptoms: Sarah started the hypokalemia nursing care plan 48 hours ago and clearly felt less symptoms like palpitations, muscular weakness, and tiredness. She said she had better athletic ability and felt more alive. Serial monitoring of serum potassium levels verified improvement.
- Improved Mobility and Stability: Based on improved muscular strength and coordination, Sarah showed more stability when ambulating over two weeks. Her potassium levels corrected to normal range, therefore supporting appropriate nerve and muscular action.
- Dietary Modifications and Medication Adherence: Sarah included in her regular diet items high in potassium, like oranges, spinach, and bananas. She also followed advised potassium supplement dosages and changed drugs according to her hypokalemia nursing care plan. She had steady potassium levels throughout follow-up visits, therefore lowering the risk of problems connected to low potassium.
By means of these assessments, Sarah’s nursing treatments for hypokalemia shown success in controlling and stabilizing her condition, thereby guaranteeing long-term well-being.
References of Nursing Care Plan Hypokalemia
- American Dietetic Association. (2021). Nutrition for medical and surgical patients. American Dietetic Association.
- American Heart Association. (2022). Cardiac monitoring and arrhythmia management guidelines. American Heart Association.
- American Society of Nephrology. (2022). Hypokalemia: Causes, symptoms, and treatments. American Society of Nephrology.
- NANDA International. (2023). NANDA-I nursing diagnoses: Definitions & classification 2023-2025. NANDA International.
- National Institutes of Health. (2023). Hypokalemia and electrolyte imbalance: Clinical guidelines. National Institutes of Health.
- National Kidney Foundation. (2023). Fluid and electrolyte balance in chronic kidney disease. National Kidney Foundation.
- World Health Organization. (2023). Global health guidelines on hypokalemia and nutrition. World Health Organization.

Well done Mr. Tahir Nazeer keep it up.
Very nice information. Outstanding 😊
Hello!
Good cheer to all on this beautiful day!!!!!
Good luck 🙂