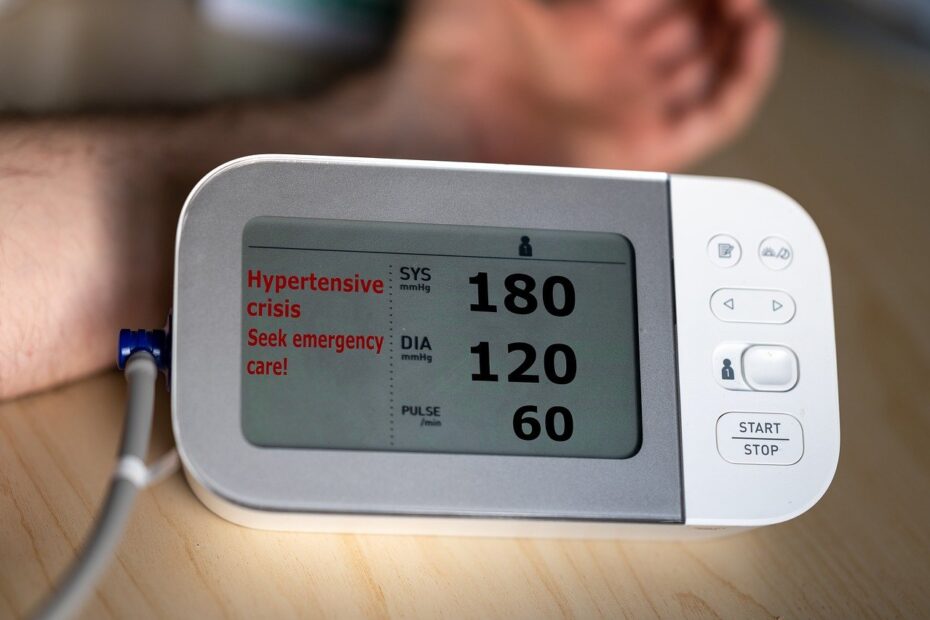
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common yet serious condition that increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. This nursing care plan on hypertension focuses on comprehensive assessment, patient education, and tailored interventions to manage elevated blood pressure and prevent complications. Effective management requires monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to antihypertensive therapy to improve patient outcomes.
You can
Patient Scenario
- Name: Mrs. Fatima Malik
- Age: 52 years
- Gender: Female
- Diagnosis: Hypertension, Stage 2 (HTN)
Scenario:
Mrs. Fatima Malik, a 52-year-old female, was admitted with persistent high blood pressure (BP), with readings consistently above 160/100 mmHg. She complains of occasional headaches, fatigue, and mild dizziness. She has a family history of hypertension and diabetes and reports a sedentary lifestyle with high salt intake.
This patient’s condition calls for a detailed nursing care plan for hypertension to address both immediate concerns like elevated blood pressure and long-term hypertension management. A well-structured care plan for HTN will include lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and symptom monitoring.
Education About Hypertension (HTN)
Definition:
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hypertension (HTN) is defined as a condition in which the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high, potentially leading to serious health issues like heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure (WHO, 2022). In any hypertension nursing care plan, educating the patient about the nature of high blood pressure is critical for promoting long-term health management.
Pathophysiology:
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) explains that hypertension occurs when there is an increase in blood pressure due to narrowing or stiffening of the arteries, leading to increased vascular resistance. This resistance forces the heart to work harder, elevating the pressure in the blood vessels. Prolonged elevated blood pressure damages the arterial walls, potentially causing complications such as heart failure, stroke, and kidney disease (NIH, 2021). Understanding the pathophysiology is a vital part of the nursing diagnosis and care plan for hypertension to ensure effective interventions.
Causes of Hypertension:
Several factors contribute to HTN, including:
- Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary behavior, high salt intake, and obesity are major contributors. These are modifiable risk factors addressed through nursing interventions for hypertension.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of hypertension increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Aging: As people age, blood vessels stiffen, raising blood pressure, which is a key factor considered in nursing care plans for hypertension.
Risk Factors:
Educating the patient about risk factors for hypertension is crucial for effective prevention and management. These include:
- Age: Individuals over 50 are at higher risk for developing HTN.
- Diet and Lifestyle: High salt intake, lack of physical activity, and obesity significantly increase the risk of elevated blood pressure. Lifestyle education forms a central part of the HTN nursing care plan.
- Genetics: A family history of hypertension heightens the risk, which is why genetic factors are considered in any hypertension NANDA nursing diagnosis.
Complications:
If left uncontrolled, hypertension can lead to several serious health complications:
- Heart Attack: High blood pressure can damage the coronary arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks.
- Stroke: Persistent elevated blood pressure raises the chances of blood clots or brain hemorrhages, making stroke prevention a focus in the nursing care plan for elevated blood pressure.
- Kidney Damage: Hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease, which underscores the need for an effective nursing care plan for hypertension to prevent such complications.
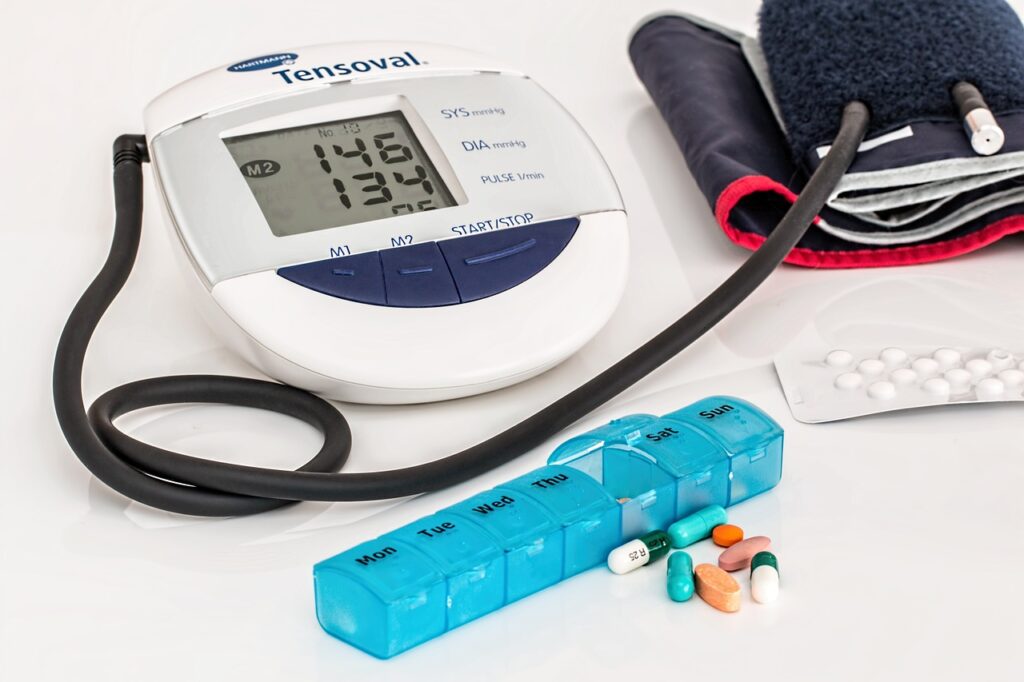
Comprehensive Assessment for Hypertension (HTN)
Assessment Components For Nursig Care Plan on Hypertension:
Blood Pressure Monitoring
- Intervention: Measure blood pressure (BP) in both arms every 4 hours.
- Rationale: Regular BP monitoring is essential in any nursing care plan for hypertension. It helps track BP trends and assess the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy. Early detection of elevated blood pressure is critical to preventing complications like stroke or heart disease, aligning with standard nursing interventions for hypertension (Smith, 2023).
- How to Perform: Use an appropriately sized BP cuff and an automated monitor. Take readings while the patient is seated and rested for at least 5 minutes. This intervention is crucial in any nursing care plan for elevated blood pressure.
Also Read: Nursing Care Plan on Insomnia
Lifestyle Assessment
- Intervention: Assess dietary habits, physical activity levels, and stress levels.
- Rationale: Identifying modifiable lifestyle factors, such as high sodium intake and lack of exercise, is critical in formulating an effective HTN nursing care plan. Lifestyle modifications are central to managing hypertension and feature prominently in the hypertension nursing diagnosis care plan (Brown, 2023).
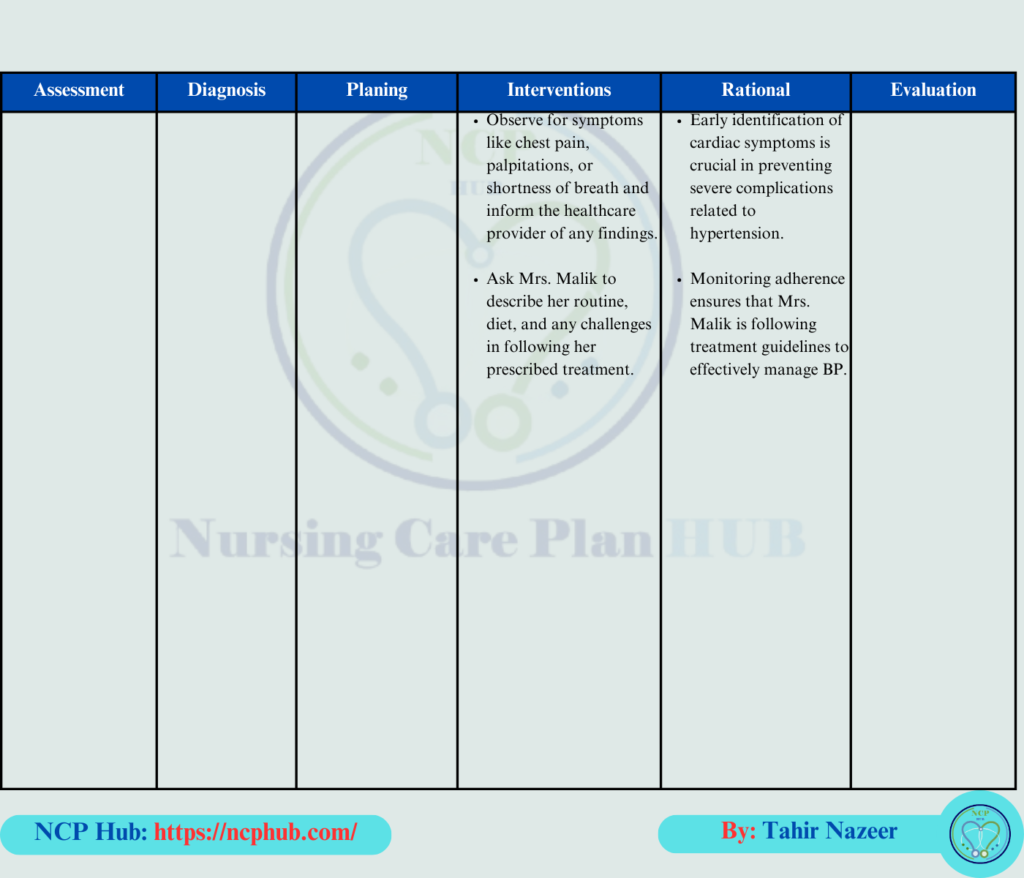
- How to Perform: Use a structured questionnaire to ask about the patient’s salt intake, exercise habits, and stress sources. Document the findings to plan personalized interventions, a key focus of nursing care for hypertension.
Cardiovascular System Assessment
- Intervention: Assess for signs of cardiovascular strain, including chest pain, palpitations, and dyspnea.
- Rationale: Hypertension can lead to heart complications such as left ventricular hypertrophy and heart failure. This makes cardiovascular monitoring a priority in the nursing care plan for a patient with hypertension, ensuring early detection of any signs of cardiac strain (Taylor, 2022).
- How to Perform: Ask the patient about any chest pain or palpitations, and assess heart rate and rhythm. Document any abnormalities, as this is a key component of the HTN nursing diagnosis and related interventions.
Neurological Assessment
- Intervention: Monitor for signs of dizziness, headaches, and visual disturbances.
- Rationale: Elevated blood pressure can impair cerebral circulation, potentially leading to neurological symptoms such as dizziness or headaches. Monitoring for these symptoms is an essential part of the nursing care plan for hypertension NANDA to prevent complications like stroke (Johnson, 2023).
- How to Perform: Ask the patient about the frequency of headaches, dizziness, or any changes in vision. Document all reported symptoms as part of ongoing neurological monitoring, which is vital in managing high blood pressure.
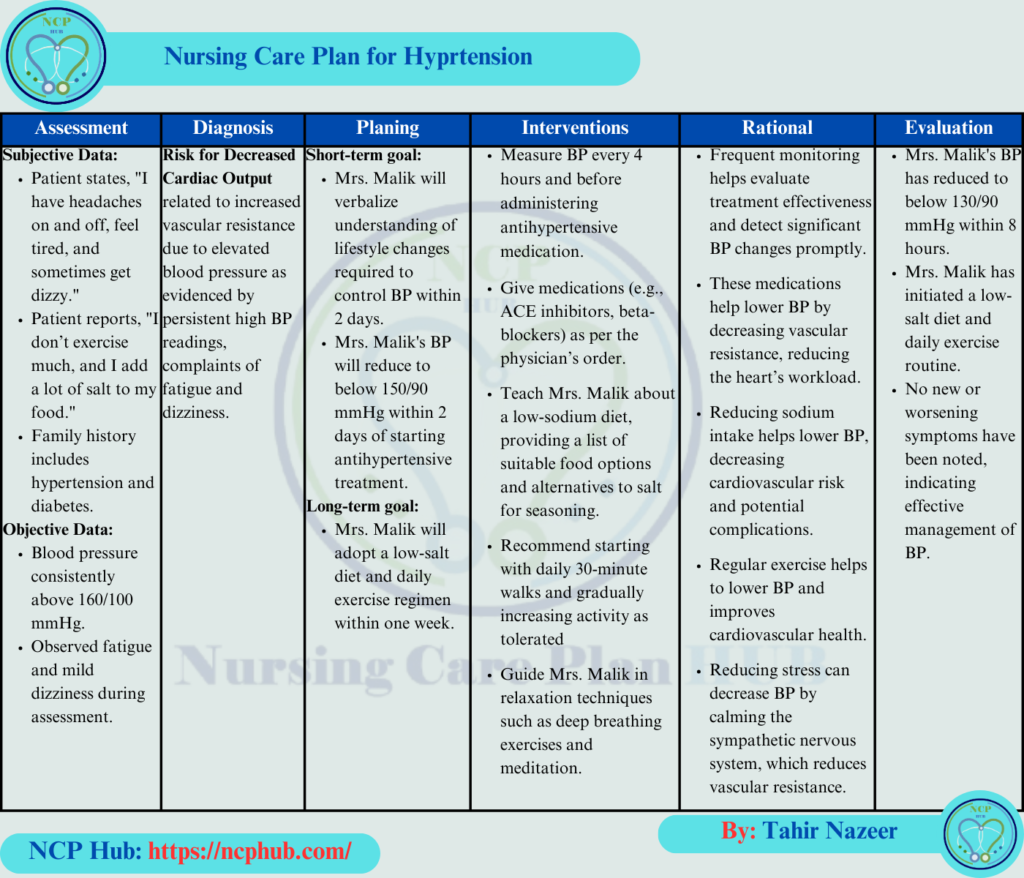
Nursing Diagnoses
Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output
- Related to: Increased vascular resistance due to hypertension.
- This is a priority diagnosis in the nursing care plan for hypertension NANDA, focusing on the potential for cardiovascular complications.
- Interventions: Monitoring for signs of heart strain and ensuring adherence to medications are crucial components of the HTN nursing care plan.
Ineffective Health Maintenance
- Related to: Knowledge deficit regarding HTN management and lifestyle modifications.
- This diagnosis is central to the hypertension NANDA diagnosis framework, focusing on the patient’s lack of understanding of hypertension management.
Planning
Short-Term Goals:
- Mrs. Malik will demonstrate an understanding of lifestyle changes required to control BP within 2 days.
- Mrs. Malik’s BP will reduce to below 150/90 mmHg within 2 days of therapy. These goals are typical in any nursing care plan for hypertension.
Long-Term Goals:
- By the end of the first week, Mrs. Malik will implement a low-salt diet and begin a regular exercise routine, reflecting effective long-term nursing care for hypertension.
Also Read: Nursing Care Plan on Fever: Hyperpyrexia and Viral Fevers
Nursing Interventions
Administer Antihypertensive Medications
- Intervention: Administer ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers as prescribed.
- Rationale: Antihypertensives help reduce vascular resistance, lowering BP, a key focus in the HTN nursing interventions.
Educate on Low-Sodium Diet
- Intervention: Provide education on a low-sodium diet.
- Rationale: Sodium reduction is a crucial component of nursing interventions for high blood pressure, as it directly affects BP management.
Monitor for Symptoms of Hypertension
- Intervention: Check for signs of dizziness, headaches, and visual disturbances, as part of nursing care for hypertension.
- Rationale: These are common symptoms of uncontrolled hypertension, making regular monitoring a standard part of a hypertension nursing plan.
Encourage Physical Activity
- Intervention: Recommend light exercise, such as walking for 30 minutes daily.
- Rationale: Physical activity is integral to maintaining cardiovascular health, forming a key intervention in a nursing care plan for HTN.
Educate on Stress Management
- Intervention: Teach stress-reduction techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, which are important in the nursing diagnosis and care plan for hypertension.
- Rationale: Stress increases sympathetic activity, raising BP. Managing stress is critical in BP control.
Evaluation
BP Control:
- Evaluate if Mrs. Malik’s BP has fallen to the target range (below 150/90 mmHg).
- Rationale: Lower BP is an indication of the effectiveness of the hypertension NANDA nursing diagnosis and interventions.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Assess compliance with diet and exercise recommendations, as part of the nursing diagnosis related to hypertension and its long-term management.
References
- Brown, J. (2023). Nursing Care Plans: A Comprehensive Guide. New York: Health Press.
- Johnson, L. (2023). Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk. Journal of Nursing Practice, 15(4), 55-63.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2021). Understanding Hypertension. Retrieved from NIH Website.
- NANDA International (NANDA-I). (2023). Nursing Diagnoses Definitions and Classification 2023-2025. Thieme Medical Publishers.
- Smith, A. (2023). Effective Blood Pressure Monitoring in Hypertensive Patients. American Journal of Nursing, 124(3), 22-28.
- Taylor, M. (2022). Stress Reduction Techniques for Hypertension Management. Nursing Standard, 38(6), 67-72.
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2022). Hypertension Management Guidelines. Retrieved from WHO Website.